Colab/Jupyter utils#
See the demo on Colab.
Lazy common imports#
Running:
from etils.lazy_imports import *
Will lazily import in the namespace 100+ common Python packages (jax, tfds, numpy, functools,…). This has 0 overhead cost as modules are only imported at first usage.
Some notes:
Colab auto-complete & cie will work as expected.
Just typing the module name in a cell can trigger an import on the background (Colab inspect the names to display metadata, like the link to source code & cie).
It is recommended to run this before any other import statement so that
import *doesn’t overwrite your imports (in case of name collision).If you
adhoc_importmodules already lazy-imported, make sure to callcolab_import.reload_packageThis should only be used in Colab.
To get the list of available modules:
List of all module aliases
lazy_imports.__all__
Mapping
<module_alias>:<lazy_module info>lazy_imports.LAZY_MODULES
Print the active imports statements (e.g. to convert lazy imports into real ones before publishing a notebook)
lazy_imports.print_current_imports()
Code at: lazy_imports.py.
Display arrays/tensors as images/videos#
By running:
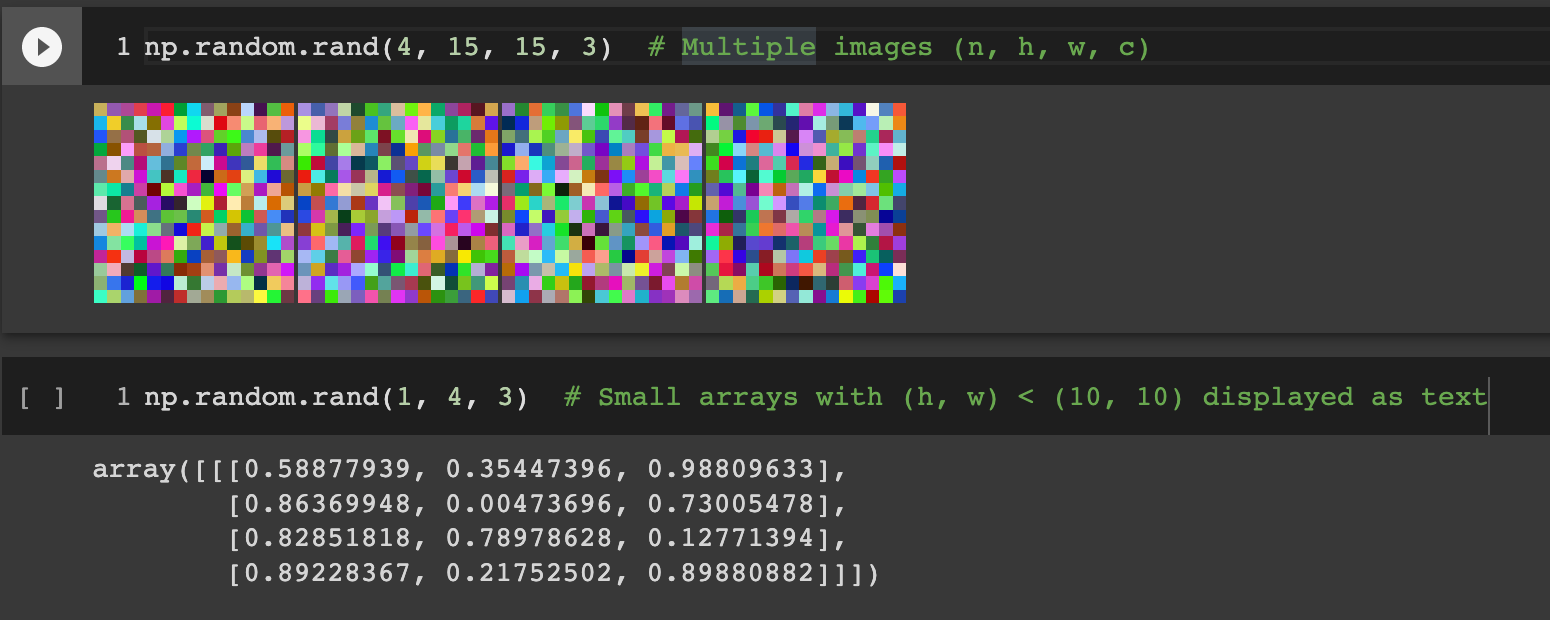
ecolab.auto_plot_array()
All ([n, ]h, w[, c]) Jax/Numpy/TF/Torch arrays bigger than (10, 10) will be
displayed as image(s)/video (if n > video_min_num_frames args, default to 15),
without having to manually call pyplot .
 {height=”220”}
{height=”220”}
The original string representation is still available through repr(array).
Pretty display with trailing ;#
Add a trailing ; to any statement (assignment, expression, return statement)
to display the current line. This call IPython.display.display() for pretty
display.
This is activated automatically when importing ecolab or lazy_imports.
Format:
my_obj;: Alias forIPython.display.display(x)my_obj;s: (spec) Alias forIPython.display.display(etree.spec_like(x))my_obj;i: (inspect) Alias forecolab.inspect(x)my_obj;a: (array) Alias formedia.show_images(x)/media.show_videos(x)(ecolab.auto_plot_arraybehavior)my_obj;p: (pretty_display) Alias forprint(epy.pretty_repr(x)). Used for pretty printdataclassesor print strings containing new lines (rather than displaying\n).my_obj;h: (syntax_highlight) Add Python code syntax highlighting ( usingecolab.highlight_html)my_obj;l: (line) Also display the line (can be combined with previous statements). Has to be at the end (;slis valid but not;ls).my_obj;q: (quiet) Don’t display the line (e.g. last line)
p, s, h, l can be combined.
x = my_fn(); # Display `my_fn()` output
my_fn(); # Display `my_fn()` output
my_fn();i # Inspect `my_fn()` output
Note that contrary to IPython default behavior, ; added to the last
statement of the cell will display the line. To silence the last output, use
;q.
An explicit API also exists:
ecolab.disp(obj, mode='sph') # Equivalent to `obj;sph`
; behavior can be disabled with ecolab.auto_display(False)
Collapsible logs on colab#
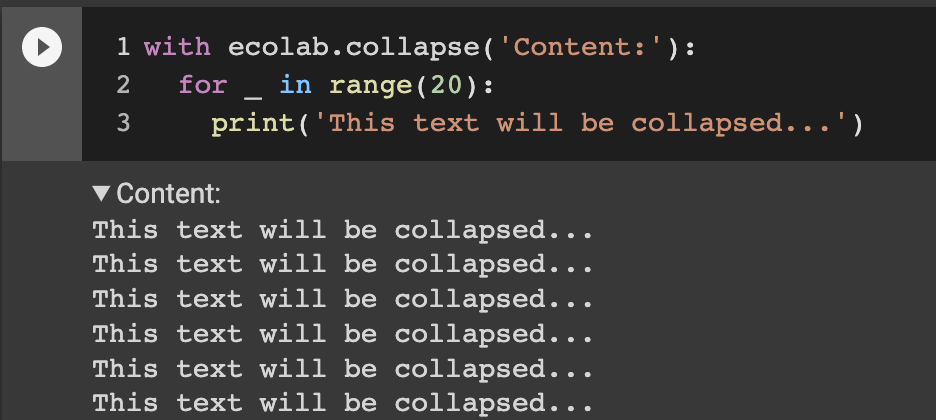
Sometimes, you might want to log verbose informations (e.g. the content of a file). To avoid polluting the logs, you can hide the logs inside a collapsible block (collapsed by default).
with ecolab.collapse('Json content:'): # Capture both stderr/stdout
print(json_path.read_text())
Example:
 {height=”180”}
{height=”180”}
Inspect any Python objects#
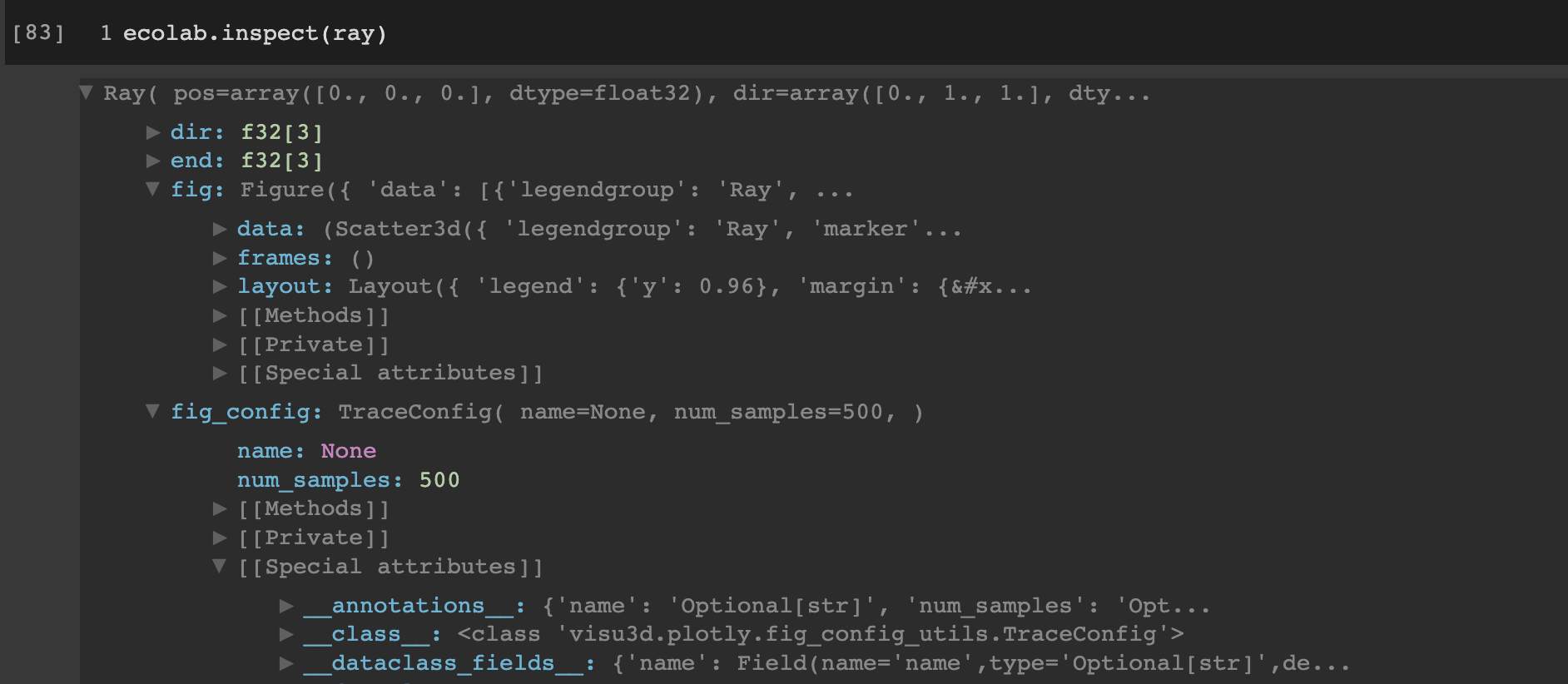
ecolab.inspect allow you to interactively explore any Python objects (e.g
module, class, dict,…), with collapsible/expandable sections.
 {height=”280”}
{height=”280”}
When developing interactively on Colab, you can add
from etils import ecolab ; ecolab.inspect(x) statements deep inside
your code, executing them will display the visualization on Colab.
To add a button in all cells to transform the last output in:
ecolab.auto_inspect()
 {height=”70”}
{height=”70”}
Inspect nested dict / list#
ecolab.json allows you to interactively explore Json nested dict / list
with collapsible/expandable sections.
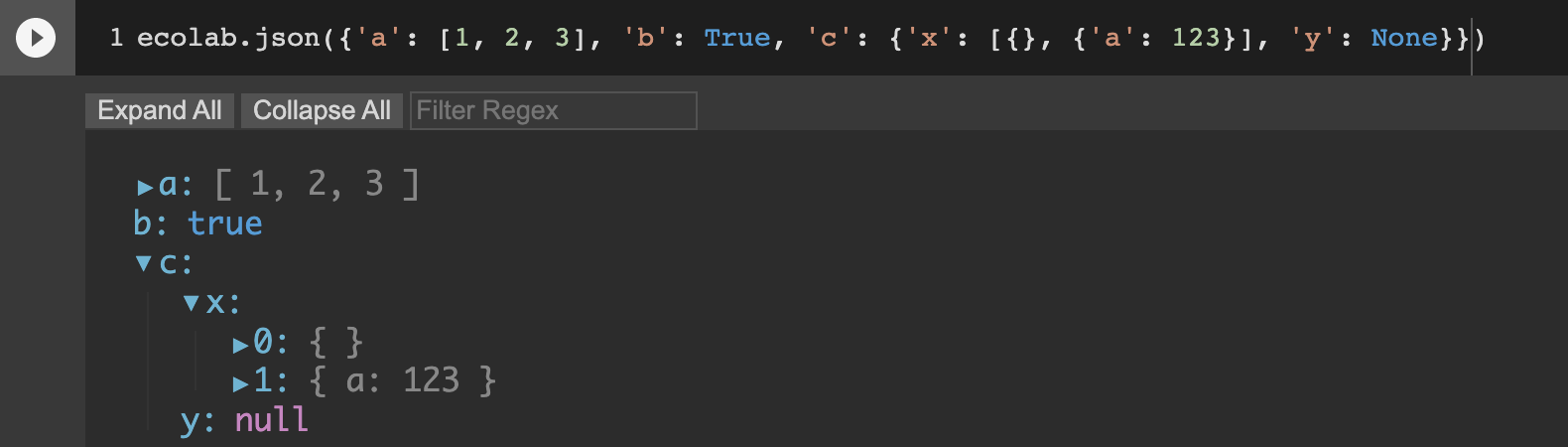 {height=”180”}
{height=”180”}
The dict keys and list indices can be filtered from the display field using
regex (e.g. x.[0-9] in the above example).
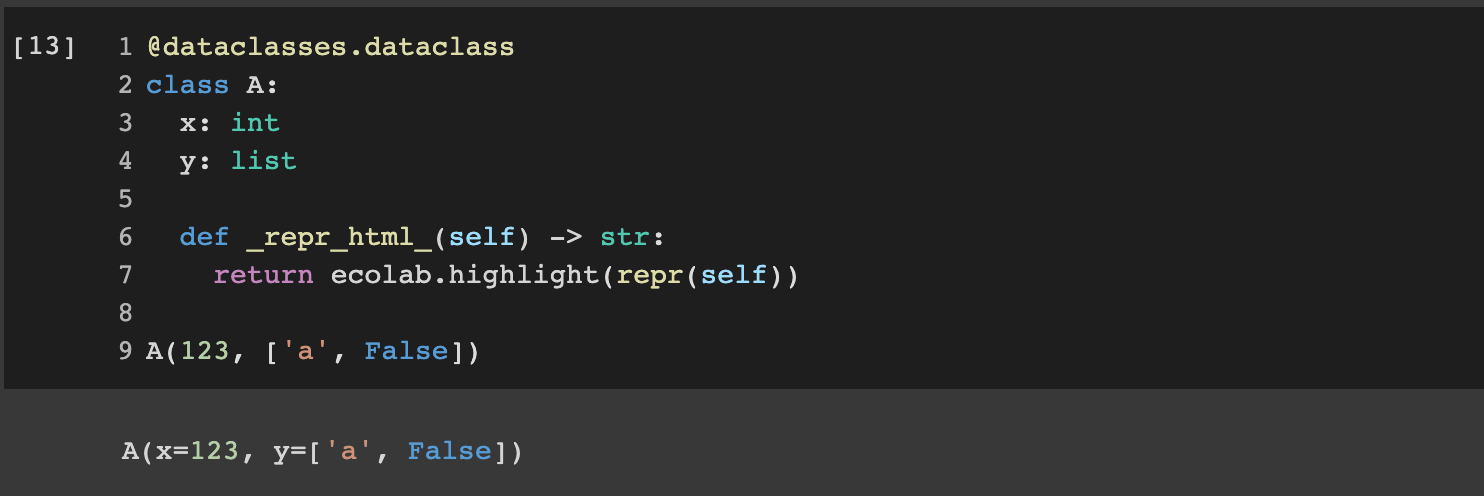
Syntax highlighting in cell output#
Use ecolab.highlight_html(code_str) to add Python syntax highlighting to a Python
code string.
Example:
@dataclasses.dataclass
class A:
x: int
def _repr_html_(self) -> str:
from etils import ecolab # Lazy-import ecolab
return ecolab.highlight_html(repr(self))
 {height=”180”}
{height=”180”}
Bi-directional Python/Javascript communication#
Ecolab provide a simplified API for Python<>Js communication which works for
both colab and jupyter notebooks.
In Python, use ecolab.register_js_fn to register any Python functions. The
function accept any json-like input/outputs (int, str, list, dict, None,…)
@ecolab.register_js_fn
def my_fn(x, y, z):
return {'sum': x + y + z}
The function can then be called from Javascript with
call_python('<fn_name>', [arg0, ...], {kwarg0: ..., kwarg1: ...})
# Currently has to be executed in the same cell to install the library
IPython.display.display(IPython.display.HTML(ecolab.pyjs_import()))
IPython.display.HTML("""
<script>
async function main() {
out = await call_python('my_fn', [1, 2], {z: 3});
console.log(out['sum']); // my_fn(1, 2, z=3) == {'sum': 6}
}
main();
</script>
""")
Interruptible loops#
ecolab.interruptible allows graceful interruption of loops. It is especially
useful for slow training loops.
While an iterator wrapped with interruptible is running, the first SIGINT
signal (e.g. from Ctrl+C or from interrupting the Colab Kernel) is captured, and
instead of raising an exception the loop simply ends after the current
iteration.
The second SIGINT signal will immediately raise a KeyboardInterrupt as usual.
# SIGINT during this loop will finish the current iteration and then
# simply stop without raising an exception raised.
for i in ecolab.interruptible(range(100)):
time.sleep(2)
print(i)
Others#
ecolab.set_verbose(): Log stderr &absl.logging(which are hidden by default)ecolab.patch_graphviz(): Makegraphvizdisplay work on Colab
Reload modules#
Helpful for interactive development to reload from Jupyter notebook the code we’re currently editing (without having to restart the notebook kernel).
Usage:
ecolab.clear_cached_modules(['visu3d', 'other_module.submodule'])
import visu3d
import other_module.submodule